vaccine delivery system review article
Increased access to misinformation through media and anti-vaccine advocacy is an important contributor to hesitancy in the United States and other high-income nations with robust immunization programs. MIT chemical engineers have developed a new series of lipid nanoparticles to deliver RNA vaccines.

Here S The Latest On Covid 19 Vaccines
There has been an increase in state-level rates of nonmedical exemptions from immunization requirements.
. April 22 2020. Research Article Free access 101172JCI116141. Antigens entrapped in such particulates when taken up by M-cells can generate immunity.
Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles microparticles or. Vaccines made from RNA hold great potential as a way to treat cancer or prevent a variety of infectious diseases. In this context several physico-chemical properties of nanoparticles play an important role in the determination of vaccine efficacy.
Paul P Fabio A. In this article we briefly review the challenges associated with current oral vaccine delivery systems and discuss strategies that might potentially target mouse and human intestinal M cells. In this Special Focus experts in the field describe recent innovations in the design evaluation and use of novel vaccine delivery devices and systems.
They have been proposed as alternatives to antibiotics for many antibiotic resistant bacterial strains. Recently it has been recognized that bacteriophages the natural predators of bacteria can be used efficiently in modern biotechnology. Shown is the efficacy of the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine in preventing Covid-19 in various subgroups within the per-protocol population.
The recent success of mRNA vaccines in SARS-CoV-2 clinical trials is in part due to the development of lipid nanoparticle delivery systems that not only efficiently express the mRNA-encoded immunogen after intramuscular injection but also play roles as adjuvants and in vaccine reactogenicity. The paper reviews why strategies and costs for HPV vaccine delivery are different from other vaccines and what is known about the cost components from available data that originated primarily from. 11 In this article we review the.
MRNA is the minimal genetic. This manuscript reviews recent developments for gene-based vaccines specifically new approaches for formulating and delivering plasmid DNA and alphaviral replicon vectors all of which have resulted in increased potency of gene-based vaccines. Immunopotentiating reconstituted influenza virus virosome vaccine delivery system for immunization against hepatitis A.
Moreover phages are used as vehicles. In parallel to their current work on a potential coronavirus vaccine researchers have developed a new vaccine delivery system for vaccines using live or. This review article focuses on the applications of nanocarrier-based vaccine formulations and the strategies used for the functionalization of nanoparticles to accomplish efficient delivery of vaccines in order to induce desired host immunity against.
One dose of an mRNA vaccine at least 28 days after an initial Johnson Johnson vaccine followed by a booster dose at least two months after the second shot. In particular they describe novel polymeric. Azizi A Kumar A Diaz-Mitoma F Mestecky J 2010 Enhancing Oral Vaccine Potency by Targeting Intestinal M Cells.
Efforts have focused on efficient delivery of vaccine antigens to mucosal sites that facilitate uptake by local antigen-presenting cells to generate protective mucosal immune responses. The COVID-19 vaccines like other vaccines work by stimulating a persons immune system to produce antibodies against the virus. A vaccine delivery system is the means by which the immune-stimulating agent constituting the vaccine is packaged and administered into the human body to ensure that the vaccine reaches the desired tissue.
Article PubMed Google Scholar JCVI statement on the annual influenza vaccination programme extension of the programme to children. A single dose COVID-19 vaccine or the first dose of the primary vaccination series for a multi -dose COVID-19 vaccine or have a pending request for or have been granted qualifying exemption or identified as having a temporary delay as recommended by the CDC. Vaccine Efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 in Specific Subgroups.
A reliable and safe vaccine delivery system. Vaccine-induced immune responses can be enhanced by mimicking the properties of pathogens. January 27 2022 staff must have received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine ie.
Considerations for school- and non-school based immunization program. Vaccine delivery systems can be classified as follows. Concerted efforts by researchers on alternative vaccine delivery routes have yielded a range of novel delivery devices with potential to enhance immunogenicity and stability.
Examples of vaccine delivery systems include. Efficient in vivo delivery can be achieved by formulating mRNA into carrier molecules allowing rapid uptake and expression in the cytoplasm reviewed in Refs 10 11. Phages can be used as biocontrol agents in agriculture and petroleum industry.
Lipidic compounds are readily recognised by the immune system and thus are ideal candidates for peptide-based vaccine delivery. Solid particulate systems such as microspheres and lipospheres are being exploited for vaccine delivery Table 1 based on the fact that intestine is an imperfect barrier to small particulates. We present an overview of mRNA delivery systems and then focus on the lipid.
Many biotech companies are now working on such vaccines and a few have gone into clinical trials. A preprint of preclinical data for Modernas coronavirus vaccine suggests it uses delivery technology that is covered by a patent owned by Arbutus and upheld last week. Introduction Vaccine acceptance is a critical component of sustainable immunization programs yet rates of vaccine hesitancy are rising.
R Glück R Mischler S Brantschen M Just B Althaus and S J Cryz Jr. Discovery of safe and effective mucosal adjuvants are also being sought to enhance the magnitude and quality of the protective immune response. Literature review of HPV vaccine delivery strategies.

How The Sinovac Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
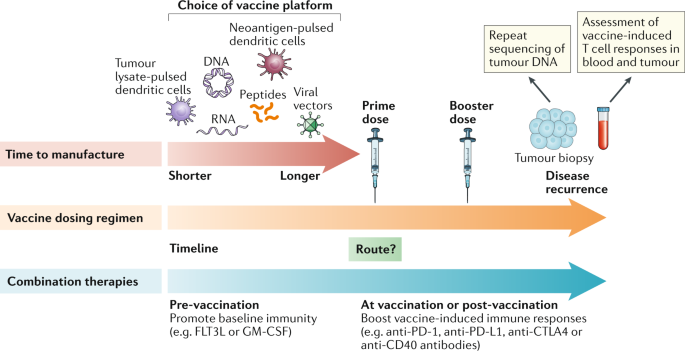
Advances In The Development Of Personalized Neoantigen Based Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology
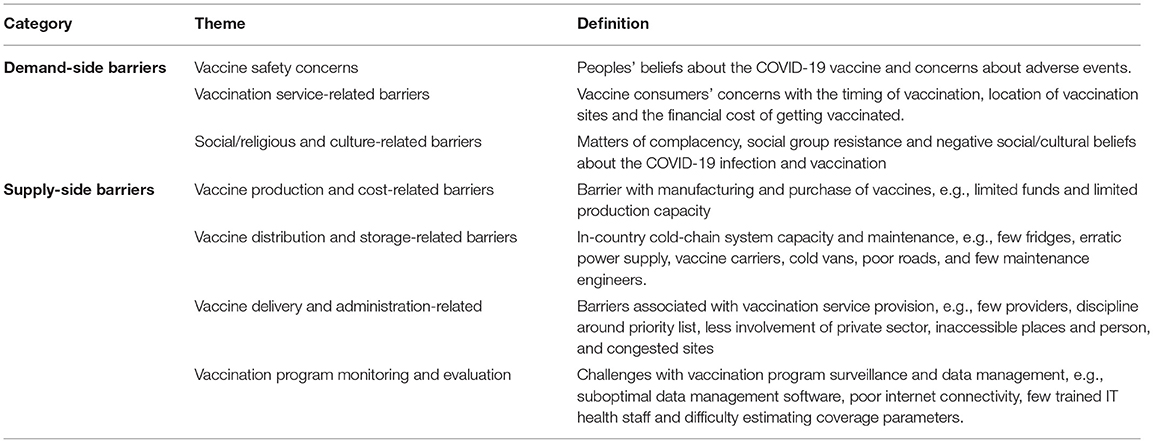
Frontiers Covid 19 Vaccination In Lower Middle Income Countries National Stakeholder Views On Challenges Barriers And Potential Solutions Public Health
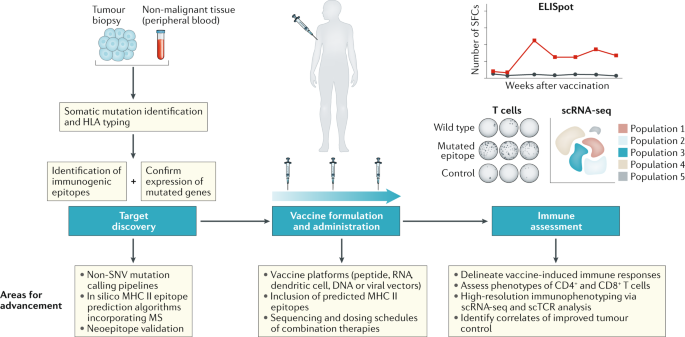
Advances In The Development Of Personalized Neoantigen Based Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology
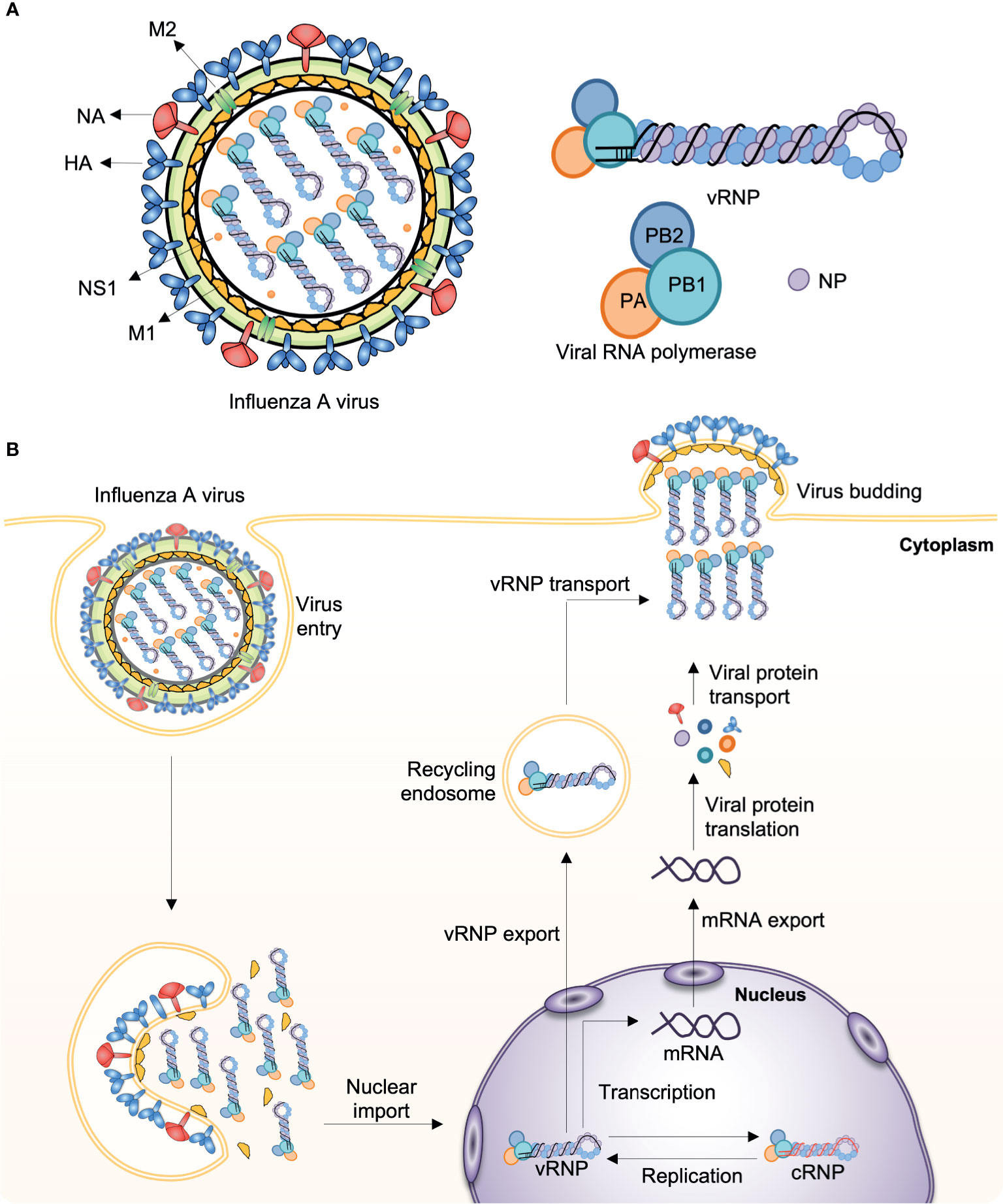
Frontiers Influenza Viruses Innate Immunity And Mrna Vaccines Immunology

Safety And Immunogenicity Of A Self Amplifying Rna Vaccine Against Covid 19 Covac1 A Phase I Dose Ranging Trial Eclinicalmedicine

Mucosal Immune Response In Bnt162b2 Covid 19 Vaccine Recipients Ebiomedicine
Covid 19 Vaccine Brand Hesitancy And Other Challenges To Vaccination In The Philippines
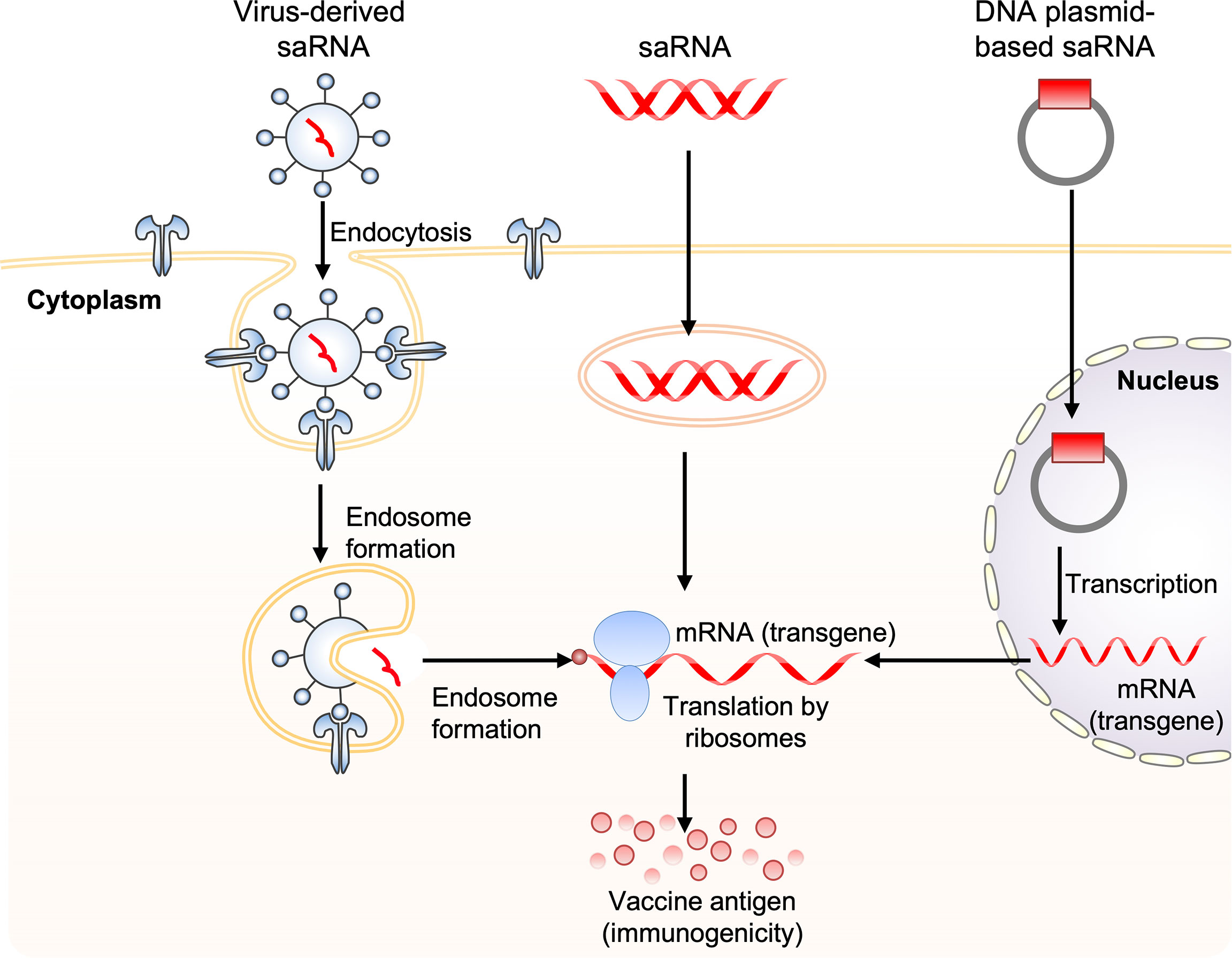
Frontiers Influenza Viruses Innate Immunity And Mrna Vaccines Immunology

Optimization Of Lipid Nanoparticles For Intramuscular Administration Of Mrna Vaccines Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
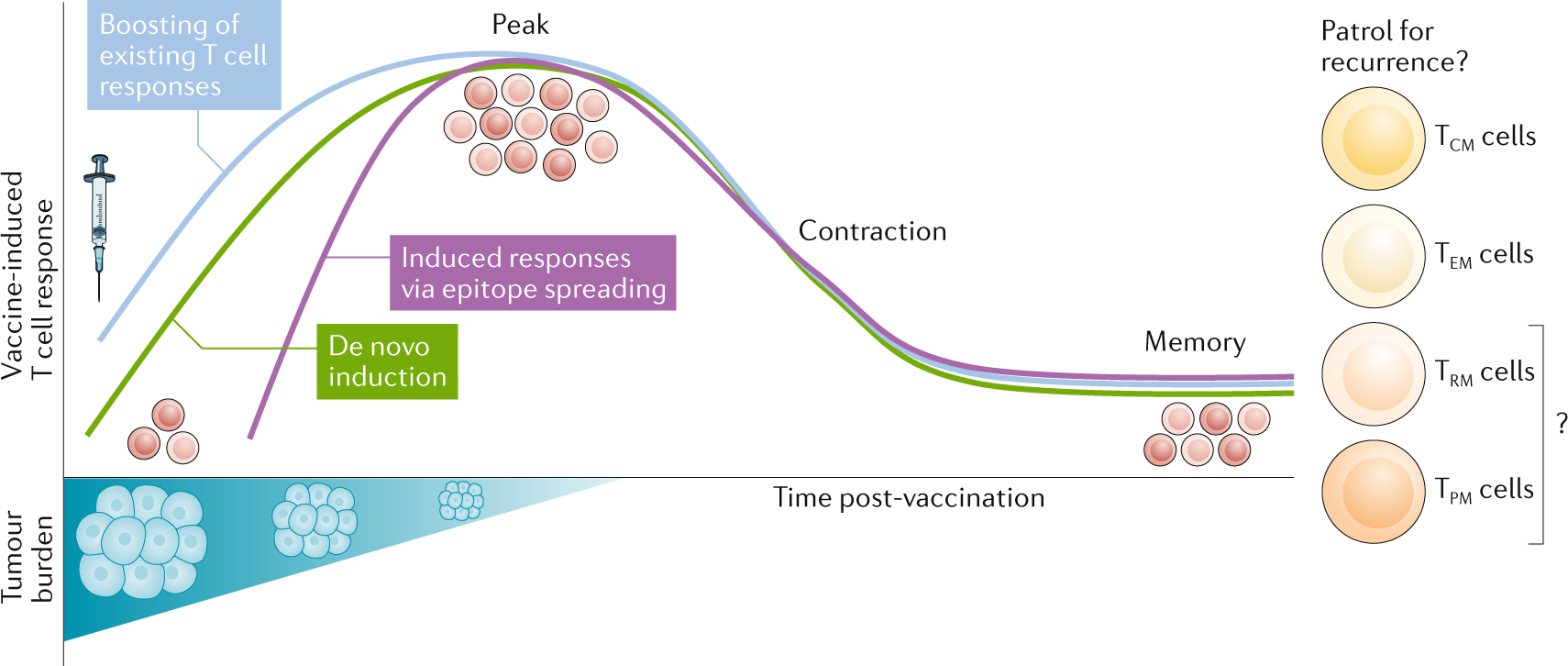
Advances In The Development Of Personalized Neoantigen Based Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology

Current And Future Nanoparticle Vaccines For Covid 19 Ebiomedicine
Covid 19 Vaccine Brand Hesitancy And Other Challenges To Vaccination In The Philippines

Vaccine Sciencedirect Com By Elsevier

Vaccination As A Preventative Measure Contributing To Immune Fitness Npj Vaccines


